Image Galleries
Featured Article
 Electron Multiplying Charge-Coupled Devices (EMCCDs)
Electron Multiplying Charge-Coupled Devices (EMCCDs)
By incorporating on-chip multiplication gain, the electron multiplying CCD achieves, in an all solid-state sensor, the single-photon detection sensitivity typical of intensified or electron-bombarded CCDs at much lower cost and without compromising the quantum efficiency and resolution characteristics of the conventional CCD structure.
Product Information
Digital Image Gallery
Fluorescence Microscopy Digital Image Gallery
Embryonic Rat Thoracic Aorta Cells (A7r5 Line)
Cellular products of the A7r5 cell line include myokinase, creatine phosphokinase, and myosin. This clonal cell line was derived by W. Carlisle from the thoracic aorta of an embryonic rat from the strain DB1X and possesses many of the properties characteristic of smooth muscle cells. The cells exhibit an increase in activity of the enzymes myokinase and creatine phosphokinase and exhibit a flat, ribbon-like morophology that differentiates into parallel arrangements of spindle-shaped cells. Many of the cells also exhibit a "fried-egg" appearance when isolated.
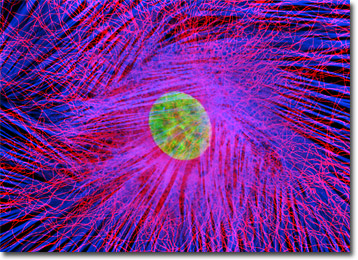
Found primarily lining the hollow organs of the body, such as the thoracic aorta from which A7r5 cells were derived, smooth muscle cells are usually arranged in dense sheets. The cells of the sheets are interconnected by gap junctions, specialized communication ports located between the cells. These junctions are composed of arrays of small channels that permit small molecules to shuttle from one cell to another, essentially linking the internal environment of one cell with those of adjacent cells. The force generating ability of smooth muscle is greater than that of other muscle types and the amount of time the force may be maintained is also significantly greater. The regulation of smooth muscle activity involves either the autonomic nervous system or hormones in the blood system. In some cases, smooth muscle tissue reacts to both types of regulation.
A7r5 cells are often utilized in medical research because smooth muscle cells are sometimes implicated in the development of various diseases and conditions. For example, an increase in smooth muscle cell size and the number of cells present in a given location have been suggested as a possible causes of hypertension, better known as high-blood pressure. According to this theory, the extra smooth muscle in the arterial walls could result in a corresponding amplification of the constrictive capacity of the artery as well as increase the thickness of the wall of the blood vessel. Both of these events could effectively constrict the artery's lumen and subsequently decrease the amount of blood flow. To counteract such an increased resistance to the flow of blood, the cardiovascular system would likely respond by raising blood pressure in order to ensure that sufficient supplies of blood were capable of reaching the many tissues of the body.
The rat thoracic aorta cells presented in the digital image above were immunofluorescently labeled with mouse anti-alpha-tubulin primary antibodies followed by goat anti-mouse secondary antibodies conjugated to Alexa Fluor 568. In addition, the specimen was stained with Alexa Fluor 350 conjugated to phalloidin and SYTOX Green, targeting the filamentous actin network and nuclei, respectively. Images were recorded in grayscale with a Hamamatsu ORCA-AG camera system coupled to an Olympus BX-51 microscope equipped with bandpass emission fluorescence filter optical blocks provided by Semrock. During the processing stage, individual image channels were pseudocolored with RGB values corresponding to each of the fluorophore emission spectral profiles.
Additional Fluorescence Images of Embryonic Rat Thoracic Aorta Cells (A7r5 Line)
Four-Color Fluorescence Labeling with Rat Thoracic Aorta Cells - In order to label the focal adhesions in the log phase adherent A7r5 culture featured in this section, the fixed and permeabilized cells were blocked and treated with mouse anti-vinculin primary antibodies followed by goat anti-mouse secondary antibodies (IgG) conjugated to Alexa Fluor 647. Filamentous actin was visualized with phalloidin conjugated to Alexa Fluor 488, while the nuclei were stained with Hoechst 33258. Prior to fixation, the cells were labeled with MitoTracker Red CMXRos for one hour to highlight the mitochondrial network.
Visualizing the Microtubule Network in A7r5 Cells - The log phase adherent A7r5 culture featured in this section was fixed, permeabilized, blocked, and treated with mouse anti-alpha-tubulin primary antibodies followed by goat anti-mouse secondary antibodies (IgG) conjugated to Alexa Fluor 568. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI.
Mitochondrial and Actin Distribution in Rat Thoracic Aorta Cells - The culture of adherent rat thoracic aorta cells presented in this section was fluorescently triple-labeled with MitoTracker Red CMXRos, Alexa Fluor 350 conjugated to phalloidin, and SYTOX Green, targeting the mitochondria, filamentous actin network, and nuclei, respectively. In this image, the bright red mitochondrial network is superimposed on a deep blue actin cytoskeletal framework centered around the green nuclei.
Cytoskeletal Features in Mammalian Fibroblast Cells - Rat thoracic aorta cells in culture (illustrated in this section) were immunofluorescently labeled with mouse anti-alpha-tubulin primary antibodies followed by goat anti-mouse secondary antibodies conjugated to Alexa Fluor 568. In addition, the specimen was stained with Alexa Fluor 488 conjugated to phalloidin and Hoechst 33342, targeting the filamentous actin network and nuclei, respectively.
Immunofluorescence Detection of Mitochondria - The adherent monolayer culture of rat thoracic aorta cells presented in this section was immunofluorescently labeled with primary mouse anti-oxphos complex V inhibitor protein antibodies, followed by goat anti-mouse Fab fragments conjugated to fluorescein. The culture was subsequently stained with Alexa Fluor 568 conjugated to phalloidin to reveal details of the filamentous actin network, and DAPI for DNA in the nucleus.
Peroxisome Localization in Fibroblast Cells - The peroxisome organelles present in the rat thoracic aorta fibroblast cell culture illustrated in this section were immunofluorescently labeled with Rhodamine Red-X conjugated to antibodies directed against peroxisomal membrane protein 70 (PMP 70). Alexa Fluor 488 conjugated to phalloidin, MitoTracker Red CMXRos and Hoechst 33258 were simultaneously used to counterstain the culture, targeting F-actin, mitochondria and DNA, respectively.
Nuclei and Mitchondria in Rat Thoracic Aorta Cells - An adherent culture of rat thoracic aorta cells (A7r5 line) was transferred to an incubation dish and treated with MitoTracker Red CMXRos and Hoechst 33258 for live-cell imaging. This combination of fluorophores highlights the proximity of nuclei and mitochondria in living cells.
A7r5 Cells with MitoTracker Red CMXRos, Alexa Fluor 488, and Hoechst 33258 - In what has become a standard fluorescence staining protocol, an adherent culture of rat thoracic aorta (A7r5) cells was labeled with MitoTracker Red CMXRos before fixing, and the cells were subsequently stained with Alexa Fluor 488 conjugated to phalloidin, followed by Hoechst 33258, a popular DNA-binding counterstain.
Visualizing Mitochondria, Peroxisomes, and the Nucleus of Fibroblast Cells - Using a triple fluoresence staining strategy to illustrate the proximity of the nucleus in reference to mitochondria and peroxisomes, A7r5 cells were immunofluorescently labeled with Alexa Fluor 647 for a peroxisomal membrane protein followed by MitoTracker Red CMXRos and DAPI.
Visualizing Mitochondria, Peroxisomes, and the Nucleus of Fibroblast Cells - In order to label the intermediate filaments in the log phase adherent A7r5 culture presented in this section, the fixed and permeabilized cells were blocked and treated with mouse anti-vimentin (porcine eye lens) primary antibodies followed by goat anti-mouse secondary antibodies (IgG) conjugated to Texas Red-X. Filamentous actin was visualized with phalloidin conjugated to Oregon Green 488, while the nuclei were stained with Hoechst 33258.