Image Galleries
Featured Article
 Electron Multiplying Charge-Coupled Devices (EMCCDs)
Electron Multiplying Charge-Coupled Devices (EMCCDs)
By incorporating on-chip multiplication gain, the electron multiplying CCD achieves, in an all solid-state sensor, the single-photon detection sensitivity typical of intensified or electron-bombarded CCDs at much lower cost and without compromising the quantum efficiency and resolution characteristics of the conventional CCD structure.
Product Information
Digital Video Gallery
Visualizing Tubulin Dynamics
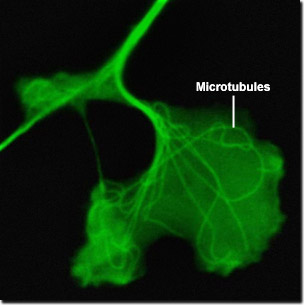
The ends of microtubules are always in dynamic formation: addition or removal of tubulin proteins alters the length of the biopolymer. The rate of depolymerization is different for each end according to its polarity, and the side that grows the fastest is considered the positive end while the other, more stable terminus, is negative. The dynamic, fast-growing portion of the microtubule is composed of beta-tubulin projected out towards the membrane of the cell. The alpha-tubulins stabilize their structure toward the nucleus at the centriole located in the centrosome of the cell. The digital videos presented in this section explore Gray fox lung fibroblast cells (FoLu line) expressing a fusion construct of mEGFP and human alpha-tubulin to highlight microtubules (green fluorescence) in order to visualize dynamic processes.
Video 1 - Run Time: 20 Seconds - Microtubule growth and extension can be clearly seen in a single fox lung cell. Choose a playback version: Streaming Video (4.7 MB), Progressive Download (4.7 MB), and MPEG Download (45 MB)
Video 2 - Run Time: 14 Seconds - A small section of the microtuble network expressing mEGFP is visible in close detail. Choose a playback version: Streaming Video (4.7 MB), Progressive Download (4.7 MB), and MPEG Download (45 MB)
Video 3 - Run Time: 14 Seconds - A large, highly concentrated collection of microtubules can be visualized in a single fox lung cell. Choose a playback version: Streaming Video (4.7 MB), Progressive Download (4.7 MB), and MPEG Download (45 MB)
Video 4 - Run Time: 20 Seconds - Microtubules are more highly concentrated in the narrow extended pseudopod of a single fox lung cell. Choose a playback version: Streaming Video (4.7 MB), Progressive Download (4.7 MB), and MPEG Download (45 MB)
Video 5 - Run Time: 20 Seconds - In addition to their structural role, microtubules function as a cell transport mechanism, as evidenced by the translocation of vesicles along the microtubules of a fox lung cell. Choose a playback version: Streaming Video (4.7 MB), Progressive Download (4.7 MB), and MPEG Download (45 MB)
Video 6 - Run Time: 20 Seconds - A large cell provides a good view of an extensive microtubule structure, as well as cell vesicles being transported along it. Choose a playback version: Streaming Video (4.7 MB), Progressive Download (4.7 MB), and MPEG Download (45 MB)