Image Galleries
Featured Article
 Electron Multiplying Charge-Coupled Devices (EMCCDs)
Electron Multiplying Charge-Coupled Devices (EMCCDs)
By incorporating on-chip multiplication gain, the electron multiplying CCD achieves, in an all solid-state sensor, the single-photon detection sensitivity typical of intensified or electron-bombarded CCDs at much lower cost and without compromising the quantum efficiency and resolution characteristics of the conventional CCD structure.
Product Information
Digital Video Gallery
Annexin Translocation in Epithelial Cells
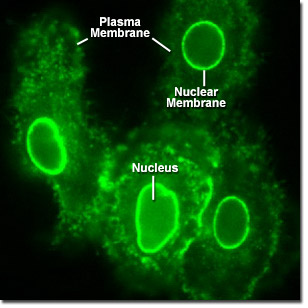
The annexin family is structurally distinct from other calcium-binding proteins, and each member consists of an N-terminal domain and a typical core domain. The core domain binds calcium and phospholipids and is comprised of four annexin repeats, each being approximately 70 residues in size. This basic core is conserved among all members of the annexin family. Through mediation of intracellular calcium signals, annexins have been demonstrated to play a role in a variety of cellular processes. The digital videos in this section illustrate the effects of calcium induction on mEGFP was fused to annexin A4 and transfected into human cervical carcinoma epithelial cells (HeLa line).
Video 1 - Run Time: 30 Seconds - Induction by ionomycin translocates mEGFP-labeled annexin (A4) from the cytoplasm to the plasma and nuclear membranes in a quartet of HeLa cells. Choose a playback version: Streaming Video (5.7 MB), Progressive Download (5.7 MB), and MPEG Download (53.7 MB)
Video 2 - Run Time: 30 Seconds - Two HeLa cells expressing mEGFP-annexin (A4) exhibit spikes external to the plasma membrane upon induction by ionomycin. Choose a playback version: Streaming Video (5.7 MB), Progressive Download (5.7 MB), and MPEG Download (53.7 MB)